Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
Jandacek divides the tutorials into three groups. In the first group are the items from antiquity: Mesolithic/Neolithic, Classical, Byzantine, Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque. In the second group are Toulouse’ contemporaries and peers: Impressionists and Post-Impressionists. In the third set are the innovations in art which took place after Toulouse died in 1901: More Post -Impressionism, Expressionism, Cubism, Surrealism, Non-Objective Etc. Because Paleolithic Art (found in the 1940s) influenced art in the 20th Century it is discussed in the post-Toulouse time.
Paleolithic
This is NOT a horse and rider. It is a horse and hunter. Horse riding had not yet been invented. Horse eating was common. Sympathetic Magic: If you capture the image well – you will also capture the animals flesh.If mare is pregnant sympathetic magic will ensure horse meat in the future. Iconoclasticism: Don’t draw your friends too realistically! It may capture their life essence (soul).
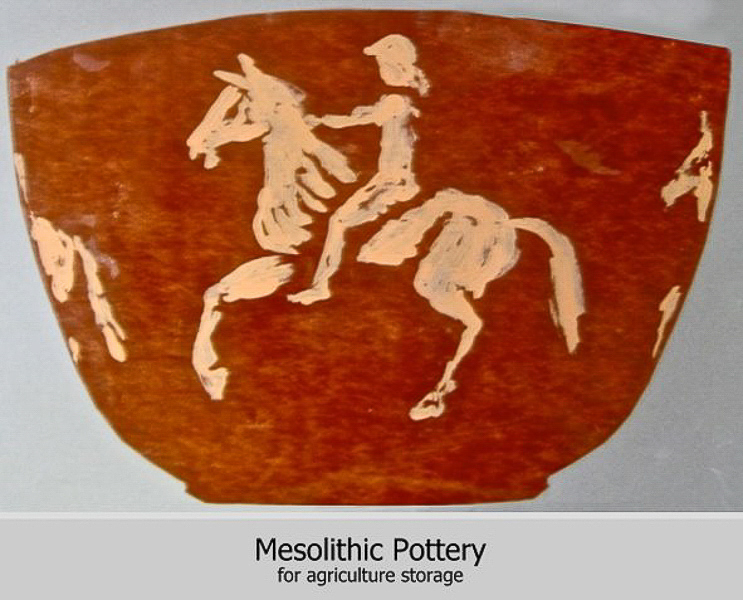
Mesolithic & Neolithic
Mesolithic & Neolithic Art is represented by pottery, basketry and weaving. Weaving and basketry use “binary” system which is employed in modern computers. Weaving looms were in fact the first computers.
Classical
Classical Art of ancient Greece and Rome is best represented by sculpture with contrapposto and triangulation. Triangulation is the re-attachment of legs and arms at distal ends to reinforce the structure and to create negative spaces. These voids tend to be triangular. Contrapposto places more weight on one foot than on the other to produce tension in the composition and twisting so that the “front” is viewed from all sides.
Byzantine
After the fall of the Roman Empire Gothic Art prevailed in the West and Byzantine Art prevailed in the East. Mosaics were the signature product of Byzantine Art. They were religious pictures made from ceramic chips. We could think of them as religious art of crackpots.
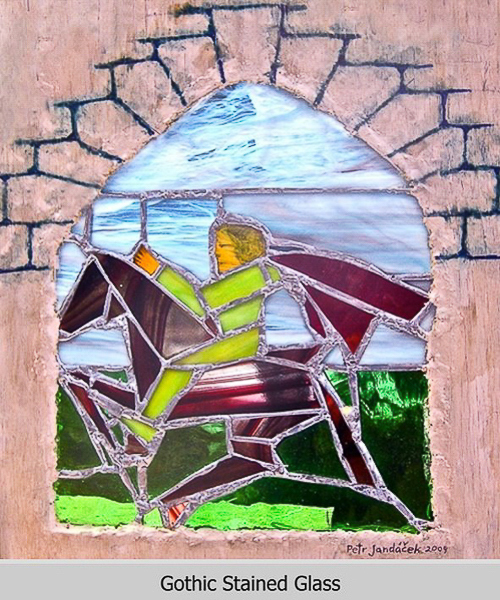
Gothic
Gothic stained glass window.
Renaissance
Renaissance perspective. Objects in distance appear smaller than in the foreground. Less emphasis on divine and saintly beings – more emphasis on merchants.
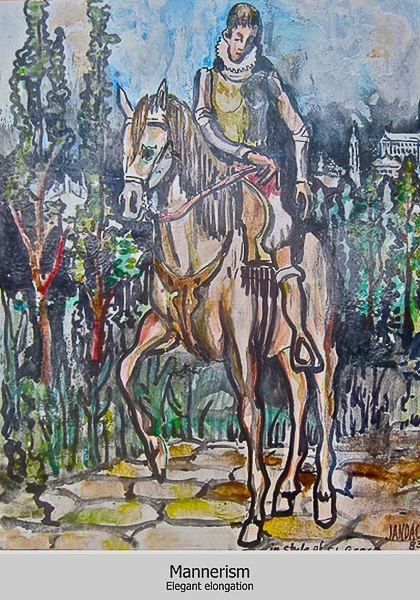
Mannerism
Mannerism (of El Greco)
Baroque
Chiaroscuro (light and dark). Pre-painted DARK canvas with light features protruding forward create illusion of great depth.
Impressionism
As a result of photography, artists (like a camera) painted LIGHT.
Pointilism
The most famous of Pointilist painter was Seurat (the Dot). Pointilism is a type of Impressionism.
Cubism
Cubism often used a monochrome (tints and shades of a single color).
Futurism
Futurism is a type of Cubism. It includes the 4th Dimension – TIME.
Geometric Expressionism
Mondrian’s De Stijl – geometric expressionism.
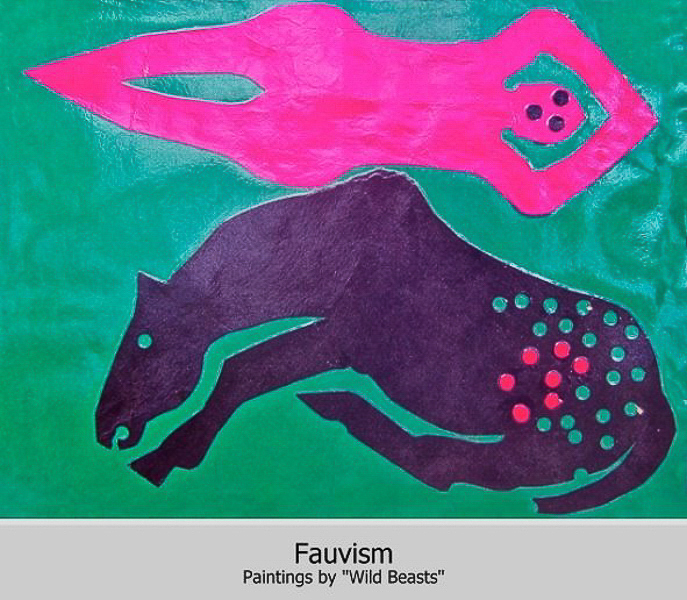
Fauvism
Emboldened by departures from traditional art, some artists used very wild colors and shapes. When they exhibited their pictures in a gallery the art experts said that the pictures looked like they were painted by wild beasts = Fauves.
Surrealism
Like in dreams, images change – from a woman to a mare, from a man to an ass. Dali made Surrealism famous.
German Expressionism
German Expressionism is made famous by the Norwegian Edvard Munch and his “Scream”.
Non-Objective Expressionism
Made famous by Jackson Pollock, Non-objective expressionism has no subject (as the name implies). Brushes make “Instrumental Art” as musical instruments produce “Instrumental Music”.
Art Noveau
Alfons Mucha represents Art Noveau. While expressionism largely de-emphasised beauty in art, Art Noveau idealized the beautiful.
(505) 672-9562
Petr Jandacek
Louise Jandacek
Mailing Address
127 La Senda Road
Los Alamos, New Mexico
USA
87544